In the world of civil litigation, the Doctrine of Res Judicata plays a crucial role in ensuring that legal battles don’t turn into endless wars. Derived from Latin, meaning “a matter judged,” this principle prevents re-litigation of cases that have already been settled. Enshrined in Section 11 of the Civil Procedure Code (CPC), 1908, Res Judicata promotes judicial efficiency, prevents harassment, and ensures that court decisions remain final and binding.
Let’s dive into the essentials of this doctrine and why it’s so important! 🔍✨
📌 What is Res Judicata?

Res Judicata simply means that once a competent court has decided a matter, it cannot be re-opened in another lawsuit. This principle upholds the integrity of judicial decisions and prevents unnecessary legal battles ⚔️.
Example: In Satyadhan Ghosal vs. Deorajin Debi, the Supreme Court of India affirmed that once a court issues a final ruling, the same parties cannot contest it again.
Key Legal Maxims
Res Judicata is governed by three fundamental legal maxims:
- Res Judicata Pro Veritate Occipitur – A judgment is accepted as the truth. ✅
- Nemo Debet Lis Vexari Pro Eadem Causa – No one should be vexed twice for the same cause. 🚫
- Interest Republicae Ut Sit Finis Litium – Litigation must come to an end for societal well-being. ⚖️
These principles ensure that judicial resources are used wisely while preventing legal harassment. 🤝
Scope of Res Judicata
Res Judicata applies across multiple legal domains:
- Civil Cases – Covers disputes under Section 11 of CPC 📜
- Criminal Cases – Prevents double jeopardy under Section 300 of Cr.P.C. 🔐
- Constitutional Law – Reinforced under Article 20(2) of the Indian Constitution 🇮🇳
🎯 Objectives of Res Judicata
- Finality of judgments – No endless litigation! 🚀
- Protection against harassment – No repeat lawsuits! ⛔
- Judicial efficiency – Saves courts’ valuable time! ⏳
Conditions for Res Judicata
For a case to be barred under Res Judicata, these conditions must be met:
- Same Parties 👥 – The disputing parties must be the same in both cases.
- Same Cause of Action ⚖️ – The core issue in both cases must be identical.
- Final Judgment 📜 – The previous judgment must be conclusive.
- Competent Court 🏛️ – The previous ruling must have been given by a court with proper jurisdiction.
Exceptions to Res Judicata

While Res Judicata ensures legal stability, some exceptions allow flexibility:
- Fraud or Misrepresentation 🕵️ – If a judgment was obtained by deceit, it can be challenged.
- Lack of Jurisdiction ❌ – If the court had no authority, the decision is void.
- New Evidence 🔍 – Strong new evidence can sometimes re-open a case.
- Example: In Jagdish Sharan Aggarwal (2009), the Supreme Court ruled that if a case was judged by an incompetent court, Res Judicata does not apply.
🤔 Res Judicata vs. Res Subjudice
- Res Judicata: Prevents cases already decided from being re-opened.
- Res Subjudice: Prevents parallel cases from being heard simultaneously. ⚖️
| Feature | Res Judicata 🏛️ | Res Subjudice ⚖️ |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Prevents re-litigation | Avoids parallel litigation |
| When Applied | After a final judgment | When multiple cases are pending |
| Effect | Bars future cases | Stays ongoing cases |
🎯 Why is Res Judicata Important?
- Saves time and resources ⏳
- Ensures consistency in court decisions 🔄
- Prevents unnecessary harassment of parties 👨⚖️
However, critics argue that it might prevent justice in some cases, especially if the first judgment was flawed.
🌟 Edzorb Law – Your Legal Companion! 📲⚖️
Want to master legal concepts effortlessly? 🏆 Edzorb Law provides:
Concise, easy-to-understand legal notes 📖
Smart summaries of case laws
MCQs & practice tests for judiciary aspirants
Expert legal insights & daily updates
🚀 Download Edzorb Law today and ace your legal studies like a pro!
Conclusion
Res Judicata stands as a pillar of the legal system ⚖️, ensuring that once a matter is decided, it is settled for good. By preventing repetitive lawsuits, it safeguards judicial efficiency and fairness in the legal process. While it has some limitations, its role in maintaining legal stability remains undeniable. 🚀
- Have questions? Drop them in the comments!
- Found this helpful?
Share with your fellow law enthusiasts! 📢
Follow Edzorb Law for much such update!

 Podcast
Podcast





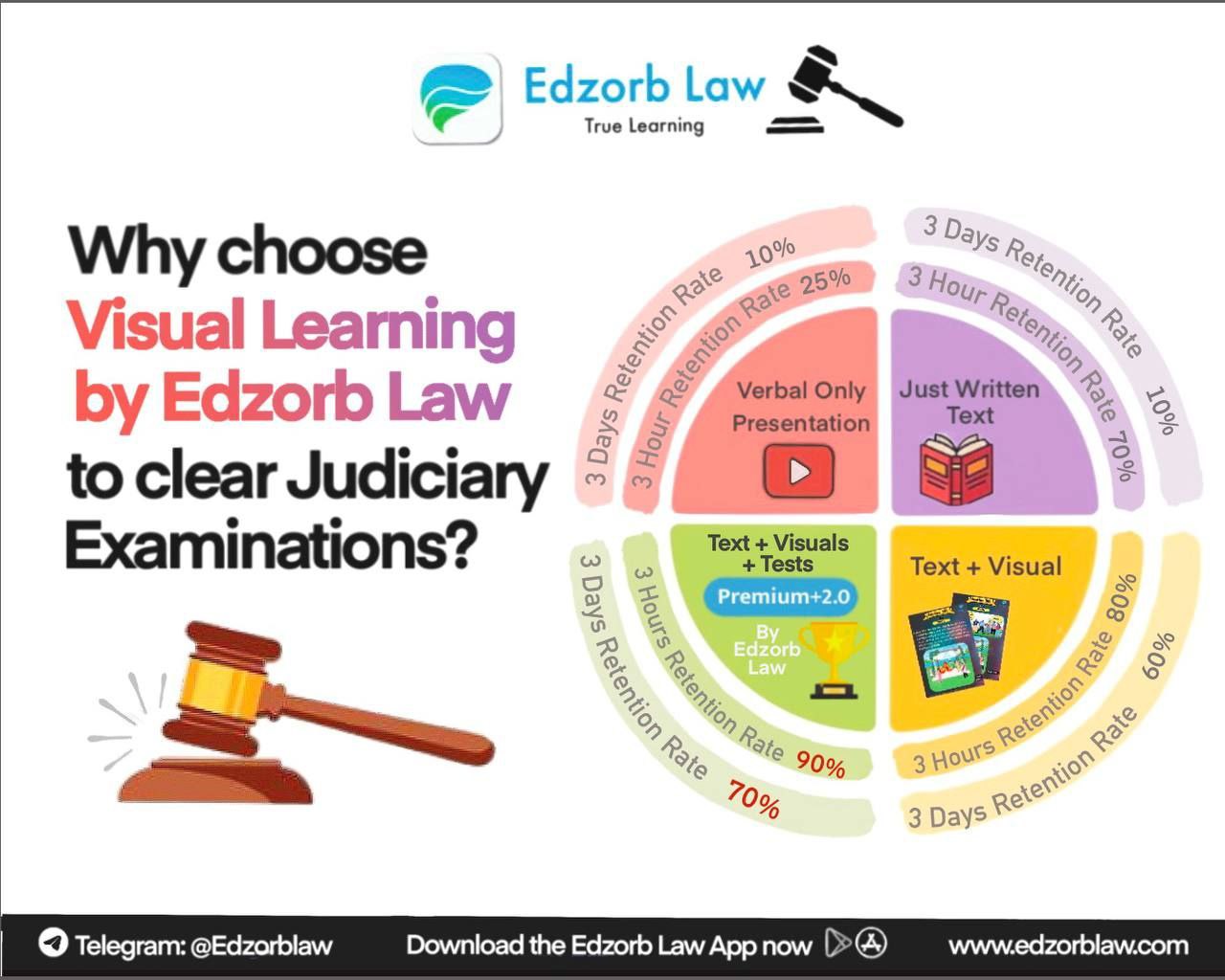
 Features
Features






