High Courts serve as the apex judicial authorities at the state and union territory levels, playing a crucial role in justice delivery.
They are empowered to uphold constitutional mandates, interpret laws, and protect fundamental rights.
Let’s explore their history, structure, jurisdiction, and powers in-depth. 🔍
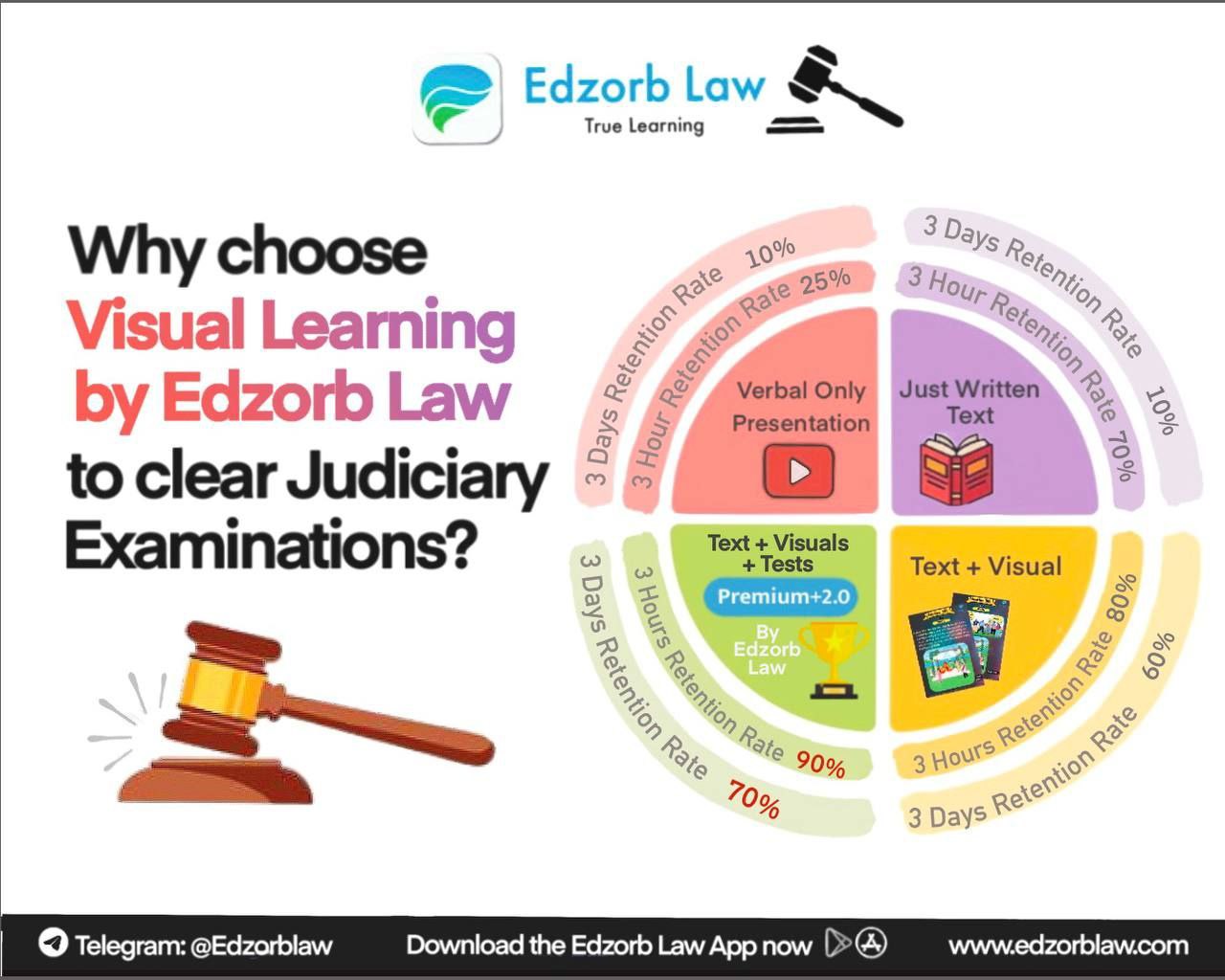
🚀 Want to ace your judiciary exam preparation?
Join Edzorb and simplify complex legal topics with crisp case summaries, mind maps, and expert insights, all designed to help you master Indian law effortlessly! 📚✅
🌐 Historical Evolution of High Courts

The Indian High Courts Act of 1861, enacted by the British Parliament, paved the way for the establishment of High Courts. The first three High Courts, Calcutta, Madras, and Bombay, were founded in 1862, replacing the older Supreme Courts and Sadar Adalats.
✅ Key Historical Milestones:
- Calcutta High Court (1862): Oldest High Court in India.
- Bombay & Madras High Courts (1862): Expanded legal governance.
- Allahabad High Court (1866): Served North-Western Provinces.
- Lahore High Court (1919): Established for Punjab.
- Delhi High Court (1966): Created post-independence.
Today, India has 25 High Courts, each playing a pivotal role in interpreting and applying the law at the state level. ⚖️
🌐 Jurisdiction & Powers of High Courts
📝 Original Jurisdiction
✔️ High Courts have original jurisdiction in civil & criminal cases (notably in Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras).
✔️ They adjudicate property disputes exceeding ₹20,000.
✔️ Empowered to issue writs under Article 226 for enforcing fundamental rights.
✔️ Handle wills, divorce, contempt of court, and admiralty cases.
🔄 Appellate Jurisdiction
✔️ Review civil & criminal appeals from district & subordinate courts.
✔️ Hear criminal appeals involving severe sentences (7+ years or capital punishment).
✔️ Examine constitutional matters involving substantial questions of law.
📚 Judicial Review Power
✔️ High Courts can strike down unconstitutional laws and executive orders.
✔️ Protect citizens’ fundamental rights through judicial intervention.
🌐 Structure of High Courts

✔️ Total: 25 High Courts across India.
✔️ Headed by: Chief Justice, assisted by other judges.
✔️ Appointment by: President of India, in consultation with CJI & Governor.
✔️ Tenure: Judges hold office until age 62.
✔️ Financial Independence: Salaries and allowances cannot be altered arbitrarily.
✔️ Post-Retirement Rules: Judges cannot hold government offices, ensuring judicial independence.
🌐 Key Functions of High Courts
✔️ Court of Record: Judgments serve as binding legal precedents.
✔️ Administrative Authority: Oversee lower courts & judicial officers.
✔️ Certification for Supreme Court Appeals: Filter cases fit for Supreme Court review.
✔️ Supervisory Role: Ensure proper functioning of subordinate courts.
✔️ Writ Jurisdiction: Issue Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Quo Warranto, & Certiorari.
🔄 Significance of High Courts
High Courts play a critical role in India’s legal system, ensuring justice, constitutional supremacy, and safeguarding rights.
✅ Interpretation of Law: Provide clarity and uniformity in legal precedents.
✅ Judicial Review: Uphold the rule of law by invalidating unconstitutional policies.
✅ Protection of Fundamental Rights: Issue writs to enforce constitutional guarantees.
✅ Supervisory Authority: Ensure efficient justice delivery in subordinate courts.
📚 Conclusion
High Courts are the pillars of justice at the state level, ensuring legal consistency, safeguarding citizens’ rights, and reinforcing constitutional values.
🚀 Want to simplify Judiciary Preparation?
Join Edzorb, where we make complex legal concepts effortless through interactive study materials, mind maps, and AI-powered judiciary prep tools! 🏆📚
👉 Ace your Judiciary Exams with Edzorb Today! 🚀

 Podcast
Podcast




 Features
Features






