2024 has been a groundbreaking year for the Indian legal system! The Supreme Court has delivered a series of landmark judgments that are already setting new benchmarks in constitutional law, civil rights, and judicial interpretation.
From high-stakes political battles to safeguarding fundamental rights, the SC’s rulings this year have redefined the legal framework and reinforced India’s constitutional values. These judgments aren’t just legal milestones, they’re shaping the future of India’s democracy and justice system. nd why they matter:
1. In Re: Alleged Rape and Murder Incident of a Trainee Doctor in Kolkata (2024)

Issue: Institutional safety measures for medical professionals.
A tragic incident at R.G. Kar Medical College, Kolkata, where a postgraduate doctor was allegedly raped and murdered during her shift, sparked national outrage. This case exposed the alarming lack of security for healthcare professionals, particularly women, in medical institutions.
Judgment:
- The SC set up a National Task Force to create and enforce a national protocol for the safety of medical professionals.
- Ordered a CBI investigation and directed the West Bengal government to report on the post-incident vandalism.
Impact:
- Improved institutional safety for healthcare workers.
- Strong message against gender-based violence at the workplace.
- Reinforced the need for systemic reforms in medical institutions.
👉 This case sets a precedent for securing workplaces and ensuring gender-sensitive policies.
2. Kuldeep Kumar vs U.T. Chandigarh (2024)
Issue: Electoral malpractice in the Chandigarh Municipal Corporation elections.
Kuldeep Kumar challenged the results of the mayoral election, arguing that eight valid votes were wrongly declared invalid, altering the election outcome.
Judgment:
- SC ruled in favor of Kuldeep Kumar after reviewing video evidence.
- Ordered proceedings under Section 340 of the CrPC against the Presiding Officer for false statements.
Impact:
- Strengthened electoral transparency and fairness.
- Reinforced judicial oversight over democratic processes.
👉 This ruling underscores the importance of electoral integrity at the grassroots level.
3. Navas Mulanavas vs State of Kerala (2024)
Issue: Sentencing in a murder case.
Navas Mulanavas, convicted of murder and sentenced to life imprisonment, appealed for leniency.
Judgment:
- SC upheld the life sentence, stating that the gravity of the offense justified the punishment.
Impact:
- Emphasized strict penalties for violent crimes.
- Balanced judicial discretion with societal interests.
👉 This case reinforces the seriousness of murder as a crime and the need for proportionate punishment.
4. Mohanlal vs State of Madhya Pradesh (2024)

Issue: Procedural lapses in an NDPS Act case.
Mohanlal was convicted under the NDPS Act but claimed procedural violations during the investigation and trial.
Judgment:
- SC acquitted Mohanlal, citing non-compliance with procedural safeguards under the NDPS Act.
Impact:
- Strengthened procedural fairness in drug-related cases.
- Reinforced the importance of upholding legal safeguards.
👉 This case highlights that due process must be followed even in stringent laws.
5. Re: Alleged Inaction of Authorities in Curbing Air Pollution in Delhi-NCR (2024)

Issue: Government’s failure to control air pollution in Delhi-NCR.
Petitioners argued that the failure to curb pollution violated the fundamental right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution.
Judgment:
- SC directed the Central and State governments to take immediate steps to reduce pollution.
- Imposed heavy penalties on non-compliant industries and strengthened enforcement of environmental laws.
Impact:
- Reinforced environmental protection as a constitutional duty.
- Established stronger judicial oversight on environmental issues.
👉 This case strengthens citizens’ right to a clean and healthy environment.
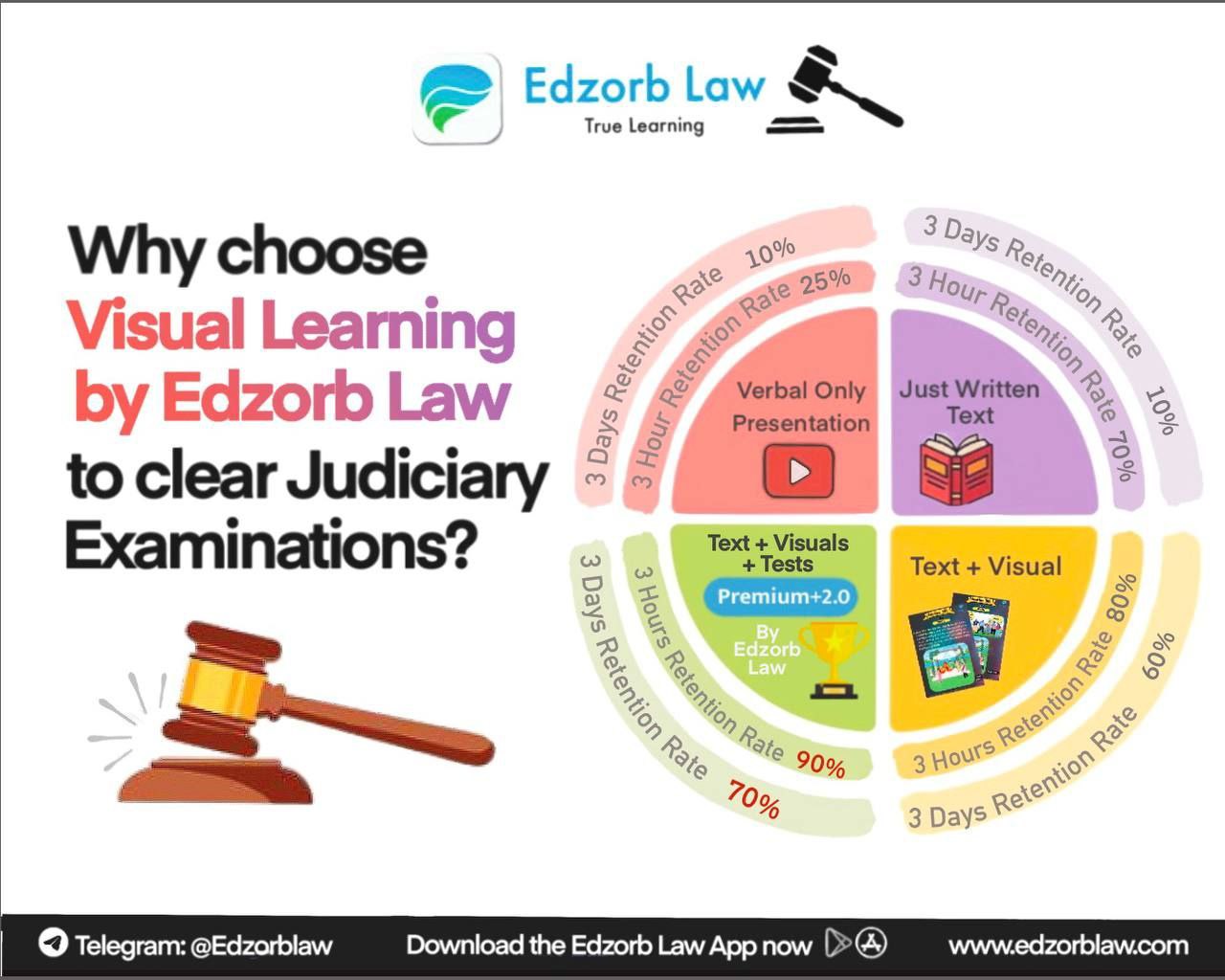
Why This Matters for Law Aspirants
These judgments reflect the evolving nature of India’s legal system and the judiciary’s proactive role in addressing complex social issues. If you’re aiming to crack the judiciary exams or want to master Indian constitutional law, these cases are must-know material!
Edzorb Law simplifies these complex rulings into easy-to-understand notes and quick revisions, helping you study smarter, not harder! Stay ahead of the curve; explore more case analyses and legal insights with Edzorb Law. Your path to mastering Indian law starts here and stay tuned for Part-II ! 🚀
📌 Bookmark this blog and Follow Edzorb Law for more legal updates and expert insights! 👨⚖️👩⚖️

 Podcast
Podcast





 Features
Features






