India’s Supreme Court has delivered some of the most influential and game-changing judgments in the history of modern democracy. These landmark rulings haven’t just interpreted the law, they’ve reshaped the very foundation of Indian constitutional values and societal norms.
Curious about how the judiciary has influenced the nation’s trajectory? Let’s explore the most impactful Supreme Court cases that have defined Indian law and democracy.
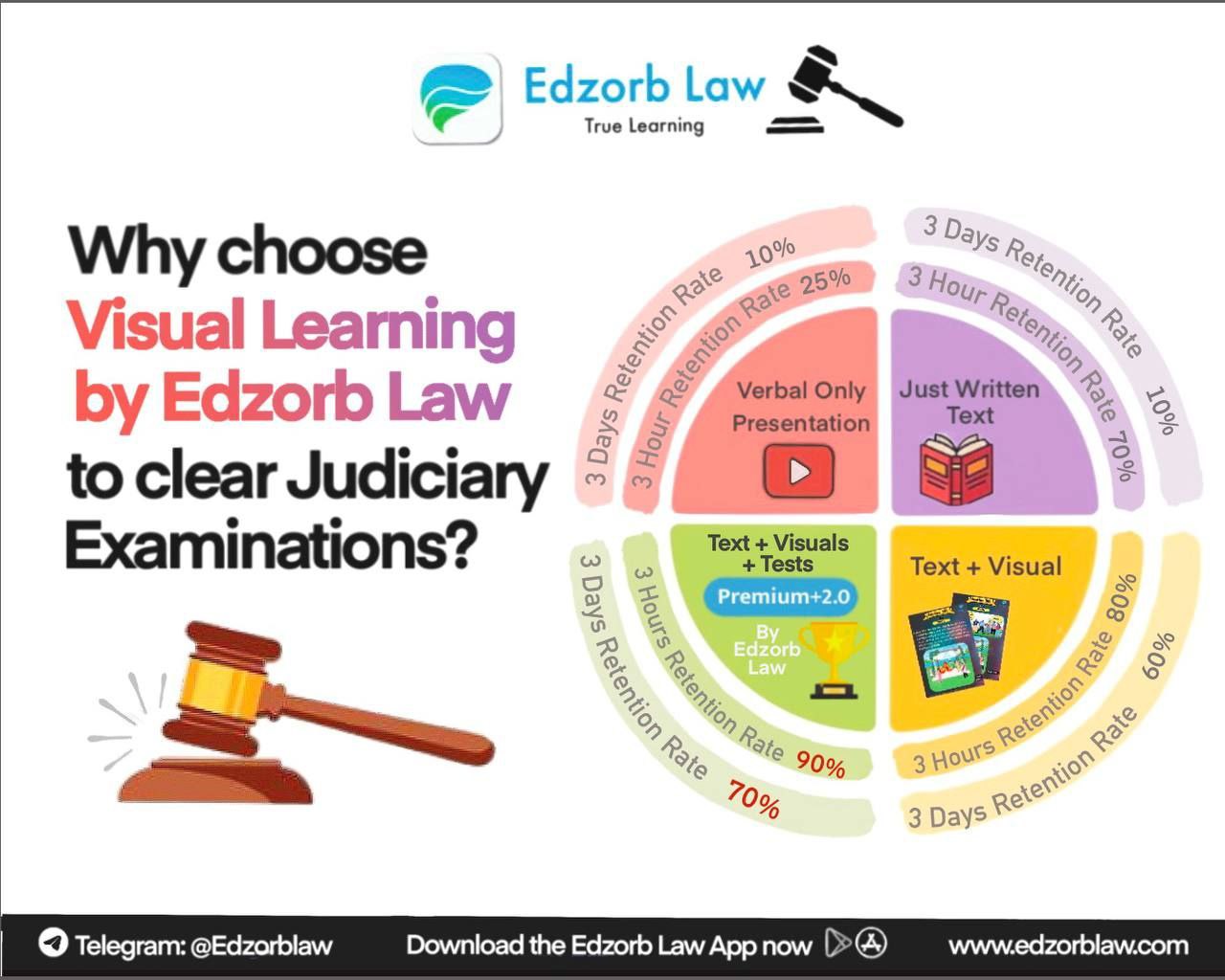
And hey, if you want to master Indian legal history the smart way, Edzorb Law has you covered!
1. A.K. Gopalan Vs State of Madras (1950): Defining Personal Liberty

Citation: (1950) SCR 88
A.K. Gopalan’s challenge to his detention under the Preventive Detention Act raised critical questions about personal liberty under Article 21. The court initially upheld a narrow interpretation, stating that as long as the procedure established by law was followed, liberty could be curtailed.
👩⚖️ Impact: While it seemed like a setback for personal freedom, this case laid the foundation for future interpretations of liberty, setting the stage for progressive rulings like Maneka Gandhi’s case.
2. Maneka Gandhi Vs Union of India (1978): Expanding the Right to Life
Citation: (1978) SCR (2) 621
When Maneka Gandhi’s passport was confiscated without explanation, the court ruled that the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 includes the right to travel and that any law restricting it must be “fair, just, and reasonable.”
👩⚖️ Impact: This case redefined Article 21 as a powerful protector of fundamental rights, expanding the scope of personal liberty to include procedural fairness.
3. Kesavananda Bharati Vs State of Kerala (1973): The Doctrine of Basic Structure
Citation: (1973) 4 SCC 225
This iconic case established that while Parliament can amend the Constitution, it cannot alter its “basic structure.” This ruling protected the core values of democracy, secularism, and fundamental rights from political overreach.
👩⚖️ Impact: The “basic structure doctrine” became a shield against constitutional amendments that threaten India’s democratic fabric, a true cornerstone of Indian democracy.
4. ADM Jabalpur Vs Shivakant Shukla (1976): Life and Liberty in Emergency

Citation: (1976) SCR 172
During the Emergency (1975–1977), the court controversially ruled that citizens could not approach courts to challenge unlawful detentions. Justice H.R. Khanna’s legendary dissent, however, stood as a beacon of judicial courage.
👩⚖️ Impact: Though criticized as a dark chapter, this ruling’s reversal in the Puttaswamy case reinforced the importance of personal liberty even during emergencies.
5. Vishaka Vs State of Rajasthan (1997): Protecting Women at Workplaces
Citation: (1997) AIR SCW 3043
Following the gang rape of social worker Bhanwari Devi, the Supreme Court laid down the Vishaka Guidelines, setting the first framework to prevent sexual harassment at the workplace.
👩⚖️ Impact: This judgment was a landmark moment for gender justice in India, eventually leading to the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act, 2013.
6. Shayara Bano Vs Union of India (2017): Triple Talaq Unconstitutional

Citation: (2017) 179 ALLINDCAS 104 (SC)
In a bold move, the court struck down the practice of instant triple talaq, declaring it unconstitutional and a violation of Muslim women’s rights under Articles 14 and 21.
💥 Impact: This ruling was a massive win for gender justice and equality within the Muslim community.
7. Navtej Singh Johar Vs Union of India (2018): Decriminalizing Homosexuality
Citation:
In a groundbreaking decision, the court decriminalized consensual homosexual relationships by striking down Section 377 of the IPC, recognizing the right to love and sexual autonomy.
🌈 Impact: This judgment was a monumental victory for LGBTQ+ rights and human dignity in India.
8. S.R. Bommai Vs Union of India (1994): Curbing the Misuse of President’s Rule
Citation:
The court ruled that the imposition of President’s Rule under Article 356 is subject to judicial review, thereby preventing its misuse for political gains.
🏆 Impact: This judgment fortified India’s federal structure and ensured that state governments cannot be arbitrarily dismissed.
9. Indra Sawhney Vs Union of India (1992): Affirmative Action and Reservation Policy
Citation: (1992) Supp (3) SCC 217
The court upheld the 27% reservation for OBCs in government jobs but introduced the “creamy layer” concept to prevent affluent sections from availing reservation benefits.
🎯 Impact: This balanced the need for social justice with merit-based opportunities, a key pillar of India’s reservation policy.
10. M.C. Mehta Vs Union of India (1987): Environmental Protection and Absolute Liability

Citation: (1987) SCR (1) 819
Following the Oleum Gas Leak, the court introduced the principle of absolute liability, holding hazardous industries strictly liable for any damage caused, without exceptions.
🌍 Impact: This ruling strengthened environmental laws and corporate accountability, setting a global precedent.
The Legacy of India’s Supreme Court
These landmark Supreme Court judgments aren’t just legal decisions, they are the building blocks of India’s democratic and legal identity. They reflect the evolving nature of Indian law and the judiciary’s critical role in protecting citizens’ rights.
📢 Want to master landmark Supreme Court cases with ease?
Unlock in-depth analysis, easy-to-understand breakdowns, and expert insights with Edzorb Law, the ultimate platform for legal mastery.
Start your journey today and become an expert in Indian law!

 Podcast
Podcast





 Features
Features






