The judiciary plays a vital role in protecting human rights by upholding the Constitution and ensuring justice for all citizens. In India, the Supreme Court and High Courts serve as the guardians of fundamental rights, defending individual freedoms and addressing human rights abuses.
What Are Human Rights?

Human rights are the inherent freedoms we’re all born with.
- Right to Life
- Liberty & Equality
- Dignity, Nutrition, Shelter, Privacy
- The right to die with dignity for terminally ill patients.
These rights are all safeguarded by Article 21, which has been expanded by the courts to cover everything essential for a life of dignity.
Rule of Law: The Backbone of Democracy
Rule of Law = No one is above the law!
- Ensures justice, fairness, and dignity for all.
Judicial Review empowers courts to strike down unconstitutional actions.
- Reinforced by landmark cases like:
- Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala
- I.R. Coelho v. State of Tamil Nadu
Separation of Powers ensures no one branch of government becomes too powerful!
Rule of Law & Human Rights: A Powerful Alliance
- Where there’s rule of law, there’s protection of human rights.
- Independent, impartial courts act as a check on misuse of power and champion fairness.
Key Judicial Responsibilities
1. Enforcement of Fundamental Rights
- Articles 32 & 226 empower citizens to approach the courts for rights violations.
- Writs are the legal weapons to defend freedoms.
2. Judicial Activism
- Maneka Gandhi Vs Union of India (1978): Expanded Article 21 to include dignity.
3. Public Interest Litigation (PIL)
- Opened court doors to the poor, marginalized, and voiceless.
- Example: S.P. Gupta Vs Union of India (1982).
4. Protection of Vulnerable Groups
- Example: Vishaka Vs State of Rajasthan (1997) – Workplace harassment guidelines for women.
5. Custodial Rights & Oversight
- D.K. Basu Vs State of West Bengal (1997) – Guidelines to prevent custodial torture.
6. Compensation & Accountability
- Courts award compensation for violations, ensuring state accountability.
Human Rights Bodies & Laws

Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993
- Established the NHRC and State Commissions (SHRCs).
- Powers include:
- Investigating complaints.
- Visiting jails.
- Promoting awareness.
The NHRC even acted on the 2002 Gujarat riots, proving its proactive role in addressing mass violations.
Landmark Cases to Remember
- Maneka Gandhi Vs Union of India (1978): Right to dignity.
- Vishaka Vs State of Rajasthan (1997): Women’s safety at workplace.
- D.K. Basu Vs State of West Bengal (1997): Custodial safeguards.
- S.P. Gupta Vs Union of India (1982): PIL revolution.
Challenges We Still Face
- Judicial Delays: 3+ crore cases pending.
- Terrorism vs Rights: A complex balance.
- Globalization: Labor rights are at risk.
- Corruption & Lack of Transparency: Public trust issues within the judiciary.
Innovations & Reforms for a Stronger Judiciary
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
- Mediation, Arbitration & Lok Adalats for faster justice.
Digitization of Courts
- E-Courts make justice faster and easier to access.
Judicial Accountability
- Ethical and transparent judiciary earns public trust.
Special Human Rights Courts & Fast-Track Justice
- Focused justice for women, children, and other vulnerable groups.
Conclusion: Judiciary = Hope for a Just India
The judiciary stands tall as the protector of liberty, dignity, and justice. Its independence, courage, and commitment are essential to keeping our democracy alive.
From gender justice to prisoner rights, from speedy trials to digital courts, the judiciary remains a beacon of hope for every Indian.
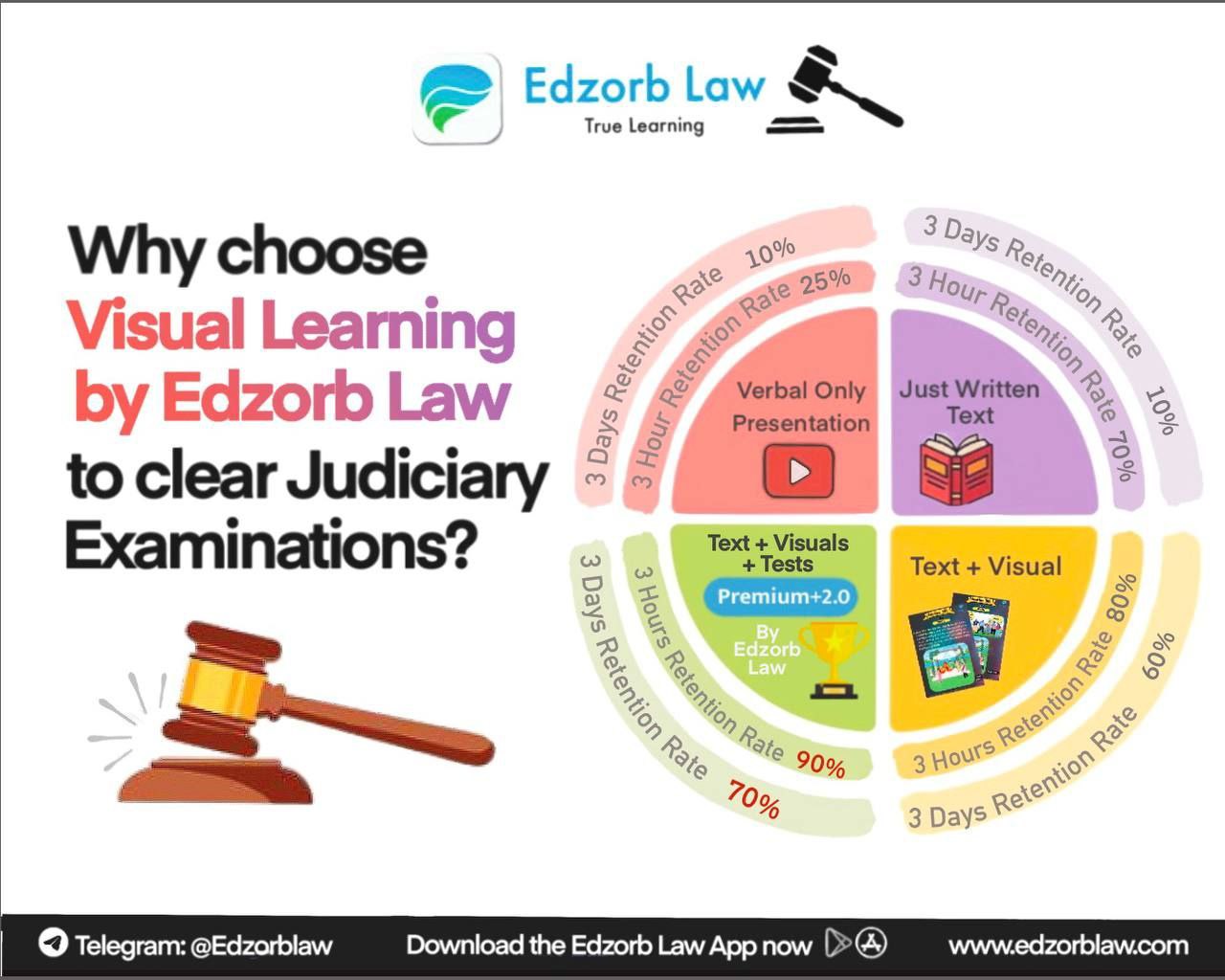
Take Charge of Your Judiciary Exam Preparation with Edzorb
At Edzorb Law, we understand the importance of human rights and constitutional law in judicial exams. Our tailored resources, interactive study materials, and expert insights will ensure you stay ahead in your preparation.
👉 Join Edzorb Law today and simplify your judiciary exam preparation with expert-curated content!

 Podcast
Podcast




 Features
Features






