Failed in college? Before panic sets in or you start doubting your worth, here’s something important to know, your grades may have dropped, but your Education rights haven’t.
Indian law offers safeguards to ensure that a failed exam doesn’t erase your educational future. Let’s unpack what your legal position is and what steps you can take and you Education Rights.
What the Indian Constitution Says About Education
-
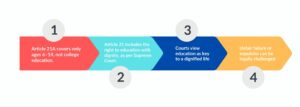
Article 21A gives every child aged 6–14 the Right to Education, but it doesn’t extend to college-level education.
-
However, the Supreme Court has interpreted Article 21 (Right to Life) to include the right to education with dignity, fairness, and opportunity, even beyond school years.
Judicial Interpretation Matters
-
Courts have held that access to education is an essential part of a dignified life.
-
If a student is unjustly failed, denied access, or expelled without procedure, it can become a legal issue.
If You’ve Failed: Can Colleges Expel You?
Colleges cannot expel you without following due process. You have the right to:
-
Be notified with reasons
-
Respond to allegations or performance issues
-
Appeal the decision through institutional mechanisms
What Do UGC Guidelines Say?
-
Universities must have Grievance Redressal Cells.
-
There must be transparent and well-defined promotion/backlog rules.
-
Disciplinary or academic decisions must be documented and communicated clearly.
Can You Legally Challenge Your Failure?
While courts avoid interfering in academic evaluations, they can step in if:
-
There’s evidence of bias or discrimination
-
Rules were not followed during exams or evaluation
-
You were denied revaluation or promotion without cause
Landmark Case: Maharshi Dayanand University v. Surjeet Kaur (2010)
The Supreme Court ruled that:
Universities must follow principles of natural justice
Arbitrary rejection of revaluation or denial of academic access violates fundamental rights
Legal Remedies Available to You
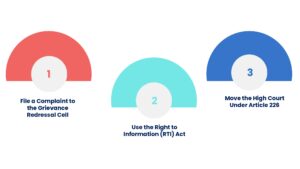
1. File a Complaint to the Grievance Redressal Cell
Each UGC-affiliated institution must have this mechanism. You can raise:
-
Unfair marking
-
Mental health-related academic issues
-
Harassment or academic bias
2. Use the Right to Information (RTI) Act
You can demand:
-
Your evaluated answer sheets
-
Marking breakdowns
-
Revaluation records
This helps ensure transparency in your results.
3. Move the High Court Under Article 226
If your college:
-
Acts unfairly
-
Violates your educational rights
-
Denies you a re-evaluation or promotion without grounds
You can file a writ petition in the High Court under Article 226.
Your Rights as a Failing Student
Even after failing, you are legally entitled to:
-
A fair opportunity to reappear or re-evaluate
-
Access to academic records
-
Freedom from discrimination
-
Mental health accommodations in line with UGC norms
Conclusion: Your Grades Don’t Define Your Legal Rights
Failing in college may feel devastating, but Indian law protects your right to continue if your failure is met with bias, unfair rules, or no due process. Know your Education Rights
Use the tools at your disposal. Ask questions. Demand fairness.
Your academic rights don’t end where your grades drop, and that’s a truth worth remembering.
📣 Want to Stay Legally Aware as a Student?
Join thousands of learners at Edzorb Law who are unlocking powerful insights into legal rights, judiciary prep, and more.
🧠 From Flashcards, Mock Tests, and Q-Bank to Visual Learning Notes; we simplify law like never before.

 Podcast
Podcast





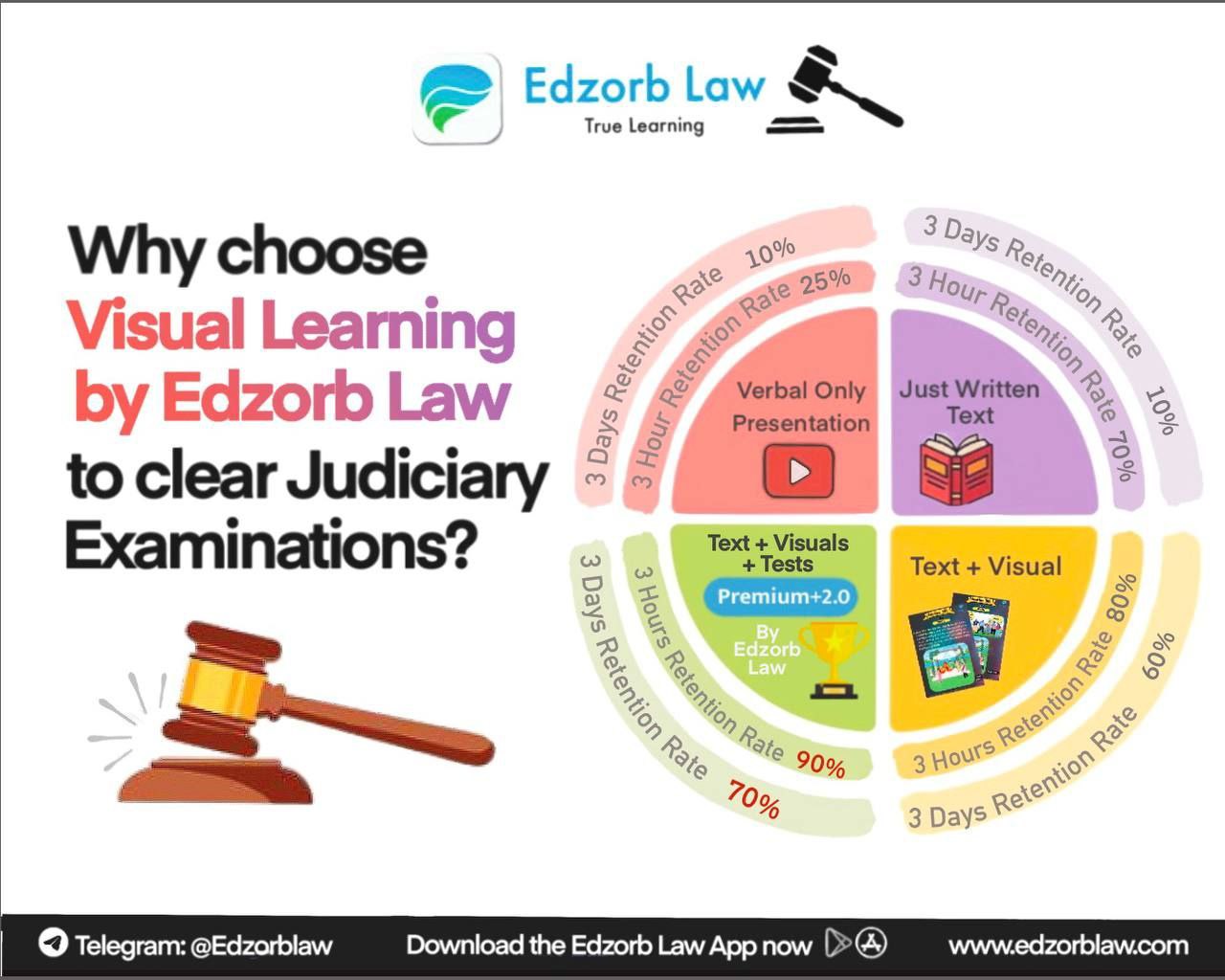
 Features
Features






