Landmark judgments are the bedrock of legal reasoning in India. Whether you’re preparing for judiciary exams, law school exams, or simply want to stay sharp in legal debates, mastering key precedents helps you score higher, argue better, and understand constitutional evolution.
Top 7 Landmark Judgments You Can’t Ignore
1️⃣ Kesavananda Bharati Vs State of Kerala (1973) AIR 1973 SC 1461
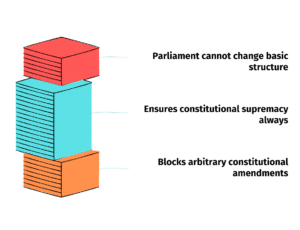
Doctrine of Basic Structure
-
Held that Parliament cannot alter the basic structure of the Constitution.
-
Secured judicial review and constitutional supremacy.
💡 Why It Matters: It’s cited in almost every constitutional law answer or essay. The basic structure doctrine is a judiciary-fortified shield against arbitrary amendments.
2️⃣ Maneka Gandhi Vs Union of India (1978) AIR 1978 SC 597
Expanded Interpretation of Article 21
-
Held that ‘procedure established by law’ must be just, fair, and reasonable.
-
Transformed Right to Life into a gateway to various human rights.
💡 Why It Matters: Strengthened due process and opened doors to right to privacy, education, and clean environment.
3️⃣ Shayara Bano Vs Union of India (2017) AIR 2017 SUPREME COURT 4609
Triple Talaq Unconstitutional Landmark Judgments
-
Declared instant triple talaq (talaq-e-biddat) as unconstitutional.
-
Upheld gender justice and women’s rights.
💡 Why It Matters: Landmark for personal laws, secularism, and women’s empowerment.
4️⃣ Navtej Singh Johar Vs Union of India (2018) AIR 2018 SC( CRI) 1169
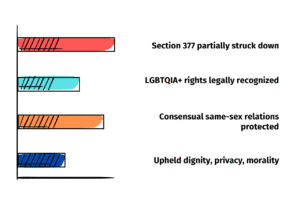
Decriminalized Section 377 IPC
-
Recognized LGBTQIA+ rights by reading down Section 377 IPC.
-
Held that consensual same-sex relations are protected under Article 21.
💡 Why It Matters: Milestone in individual dignity, privacy, and constitutional morality.
5️⃣ Vishaka Vs State of Rajasthan (1997) 1997(6) SCC 241
Workplace Sexual Harassment Guidelines
-
Laid down the Vishaka Guidelines on preventing sexual harassment at workplaces.
-
Filled legislative gaps using international conventions.
💡 Why It Matters: Foundation for POSH Act, 2013 and gender-sensitive workplaces.
6️⃣ Indra Sawhney Vs Union of India (1992) 1992 Supp (3) SCC 217
Reservation Cap and Creamy Layer Doctrine
-
Upheld OBC reservations, capped reservations at 50%, and introduced creamy layer exclusion.
💡 Why It Matters: Essential for reservation debates, equality, and affirmative action.
7️⃣ Justice K.S. Puttaswamy Vs Union of India (2017) AIR 2017 SUPREME COURT 4161
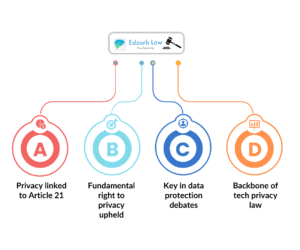
Right to Privacy is a Fundamental Right
-
Privacy was declared as part of Right to Life under Article 21.
-
Crucial for debates on data protection, Aadhaar, and digital surveillance.
💡 Why It Matters: Forms the constitutional backbone for privacy and tech law.
Quick Revision Table
| Case Name | Key Principle | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Kesavananda Bharati | Basic Structure Doctrine | 1973 |
| Maneka Gandhi | Due Process under Article 21 | 1978 |
| Shayara Bano | Triple Talaq Unconstitutional | 2017 |
| Navtej Johar | LGBTQIA+ Rights & Section 377 | 2018 |
| Vishaka | Workplace Sexual Harassment Guidelines | 1997 |
| Indra Sawhney | Reservation Cap & Creamy Layer | 1992 |
| Puttaswamy | Right to Privacy | 2017 |
Case Crunch Tip
Use mnemonics to remember judgments – e.g., “KMS VIP NP” = Kesavananda, Maneka, Shayara, Vishaka, Indra, Puttaswamy, Navtej.
💬 Pro Tip: Practice one-liner summaries and case-based MCQs on Edzorb Law Visual Learning Notes and Flashcards.
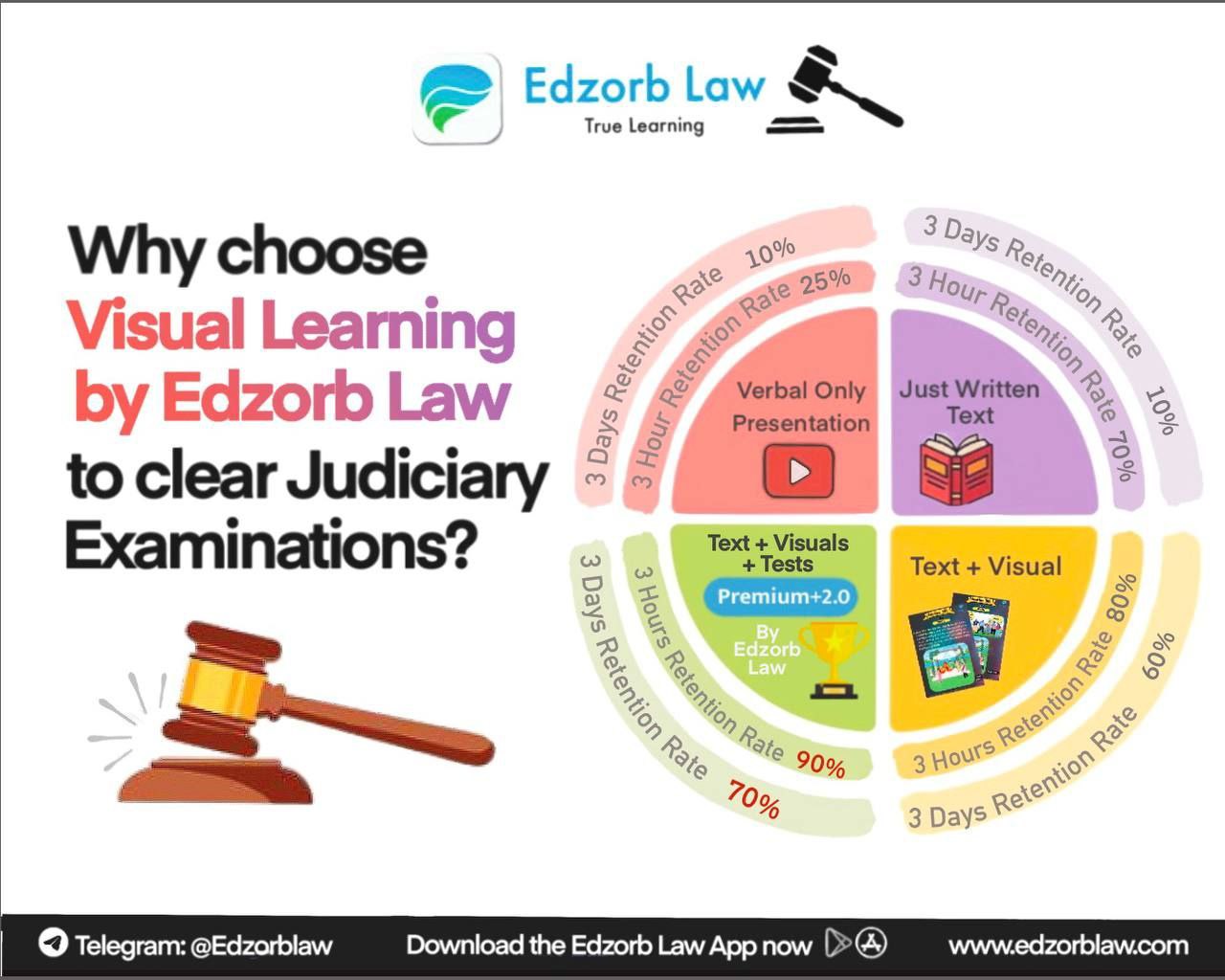
🎯 Why Mastering These Cases Is a Gamechanger
-
Judiciary exams frequently ask match the case with principle questions.
-
Essay papers demand critical discussion of precedents.
-
Moot courts and internship interviews favor students who quote leading cases.
📲 Learn Faster with Edzorb Law
Struggling to memorize all these cases?
🚀 Edzorb Law’s Visual Learning Notes, Case Flashcards, and Mock Tests make learning binge-worthy and retention-proof.
🔹 Daily Case Crunch Quizzes
🔹 Judgment Infographics
🔹 Personalized Study Planners
👉 Join Judiciary Aspirants leveling up their prep with Edzorb Law.

 Podcast
Podcast



 Features
Features






