Are you a judiciary aspirant ready to conquer Procedural Law with confidence? 🚀 This subject forms the backbone of the justice delivery system and plays a pivotal role in ensuring fair trials and legal processes.
In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through important sections, landmark judgments, and smart strategies to master Procedural Law. Let’s get started on your journey to success!
Understanding the Importance of Procedural Law

What is Procedural Law?
Procedural law, also known as adjective law, consists of rules and processes that courts follow to adjudicate cases. It ensures that justice is administered fairly and regulates legal proceedings.
Relevance in Judiciary Exams
✔ Procedural law frequently appears in judiciary exams because it governs court procedures.
✔ It is essential for answering questions on court processes, justice administration, and legal rights enforcement.
Start with the Basics: Core Procedural Laws
Key Legislations
Familiarize yourself with the primary procedural laws in India:
- Code of Civil Procedure (CPC) – Governs civil case procedures.
- Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) – Governs criminal case procedures.
- Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA) – Regulates the admissibility of evidence in court.
Importance of Both Civil & Criminal Procedures
Judiciary exams test both civil and criminal procedures. A strong grasp of these laws helps navigate diverse legal scenarios.
Focus on Legal Proceedings: Structure & Stages
Civil Proceedings
✔ Institution of Suit: Filing a civil suit, including pleadings, summons, and service of process.
✔ Trial Procedures: Examination, cross-examination, and role of evidence in civil trials.
✔ Judgment & Decree: Delivery of judgments, significance of decrees, and execution process.
Criminal Proceedings
✔ Filing of FIR & Charge Sheet: Procedures for FIR lodging, investigation, and charge sheet filing.
✔ Bail Procedures: Different types of bail and their legal conditions.
✔ Trial Process: Framing of charges, witness examination, and final arguments.
Master Procedural Law Through Landmark Cases
Key Case Laws
✔ Kesavananda Bharati Vs State of Kerala (1973) – Understanding the balance between substantive & procedural laws.
✔ A.R. Antulay Vs R.S. Nayak (1988) – Important case on procedural rights of the accused.
Application in Exams
Citing landmark cases in answers shows deep understanding and demonstrates legal application skills.
Regularly Practice Writing Case Briefs
Summarizing Judgments
Writing case briefs helps condense complex judgments into concise summaries. Focus on:
✔ Procedural aspects
✔ Application of laws
✔ Court reasoning
Mock Trials & Moot Courts
Participate in mock trials & moot courts to gain practical experience in procedural law.
Stay Updated with Amendments & Developments

Keep Track of:
✔ Recent amendments.
✔ Latest Supreme Court & High Court rulings.
✔ Evolving interpretations of procedural laws.
Use the Right Study Materials
Standard Textbooks
✔ Mulla’s Code of Civil Procedure
✔ Ratanlal & Dhirajlal’s Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita
Bare Acts & Commentaries
Reading Bare Act and legal commentaries provides clarity and practical insights.
Join Study Groups & Discussions
Benefits:
✔ Collaborative learning – Share insights and clarify doubts.
✔ Mock interviews & group discussions – Essential for viva voce preparation.
✔ Current legal trends – Stay updated through peer discussions.
Practice Past Years Judiciary Exam Papers
Key Strategies:
✔ Analyze past exam patterns to understand frequently tested topics.
✔ Practice answer writing to develop structured and concise responses.
✔ Time management techniques for improved efficiency.
Conclusion: Your Roadmap to Judiciary Success
Studying procedural law for judiciary exams doesn’t have to be overwhelming!
Follow this step-by-step guide to:
✔ Organize topics effectively
✔ Memorize key sections with ease
✔ Strengthen your legal reasoning skills
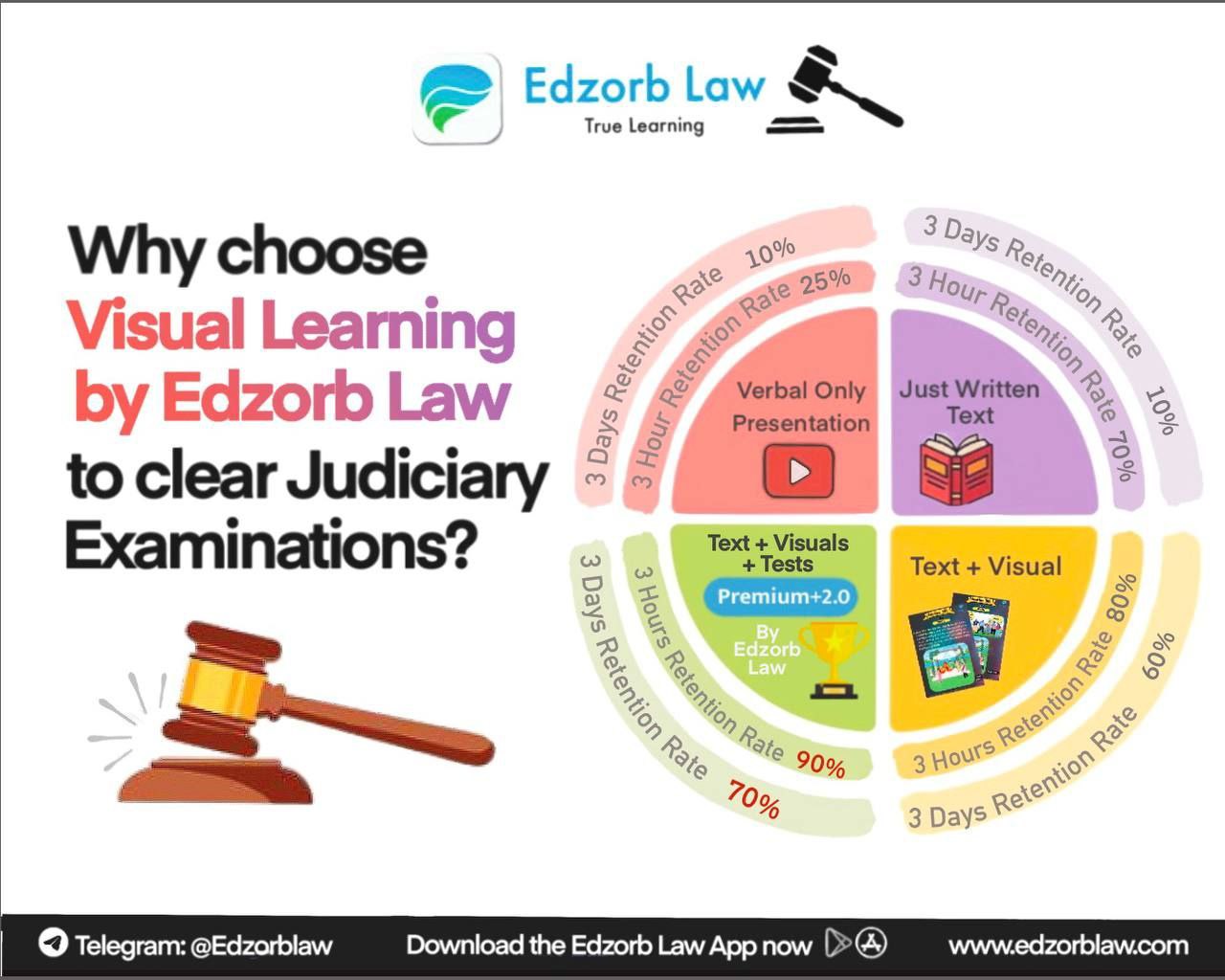
Looking for a Smarter Way to Study Procedural Law?
Edzorb Law has got you covered!
- Visual Learning Notes for quick retention
- Mind maps to simplify complex topics
- Interactive learning for better recall
🚀 Ace your judiciary exams with Edzorb Law!
Join Edzorb Law today & take your procedural law prep to the next level! 🔥💪

 Podcast
Podcast




 Features
Features






