Judicial discretion is the power granted to judges to make decisions based on their understanding of the law, facts, and equity of a case.
However, while judicial discretion enables courts to interpret and apply laws to unique circumstances, it must be exercised with caution.
Constitutional Provisions on Judicial Discretion
Several key articles of the Indian Constitution grant discretionary powers to the Supreme Court, empowering it to make decisions that ensure justice and fairness.
Article 139(A) gives the Supreme Court the authority to transfer cases from one High Court to another. This power ensures that justice is served impartially, especially in cases where there may be concerns of bias or when it is necessary to maintain the balance of the legal system across jurisdictions.
Scope and Limits of Judicial Discretion

Though judicial discretion is extensive, it is not without limitations:
Article 136: The Supreme Court can entertain appeals even after other avenues of appeal are exhausted. However, it is intended to be used sparingly, only for cases involving substantial legal questions or instances where grave injustice has occurred.
Article 142: This article allows the Supreme Court to pass orders for complete justice. However, its use is not unlimited. The Court has clarified that it should supplement existing laws but should never contradict them.
Should There Be Judicial Review of Discretionary Powers?
Given the extraordinary nature of these powers, judicial review is crucial to prevent their misuse. Courts must establish clear guidelines for the exercise of discretionary powers to preserve the integrity of the judiciary and maintain a balance of power between the branches of government.
Areas of Judicial Discretion
Judges exercise discretionary powers in several areas:
- Sentencing: Judges determine appropriate punishments, considering the nature of the offence and the circumstances of the accused.
- Bail: Judges decide whether to grant bail in non-bailable offences, based on factors like the likelihood of reoffending.
- Injunctions: Judges have the discretion to grant temporary injunctions, considering the case specifics and potential harm to the parties involved.
Contemporary Issues and Challenges

Despite its importance, judicial discretion brings certain challenges:
Potential for Overreach: Cases like the coal block cancellation in 2014 have raised concerns about judicial overreach, with the Court potentially overstepping into legislative territory.
Lack of Clear Guidelines: Without clear guidelines, judicial discretion can lead to inconsistent and arbitrary decisions, potentially undermining the rule of law.
Critical Analysis and Conclusion
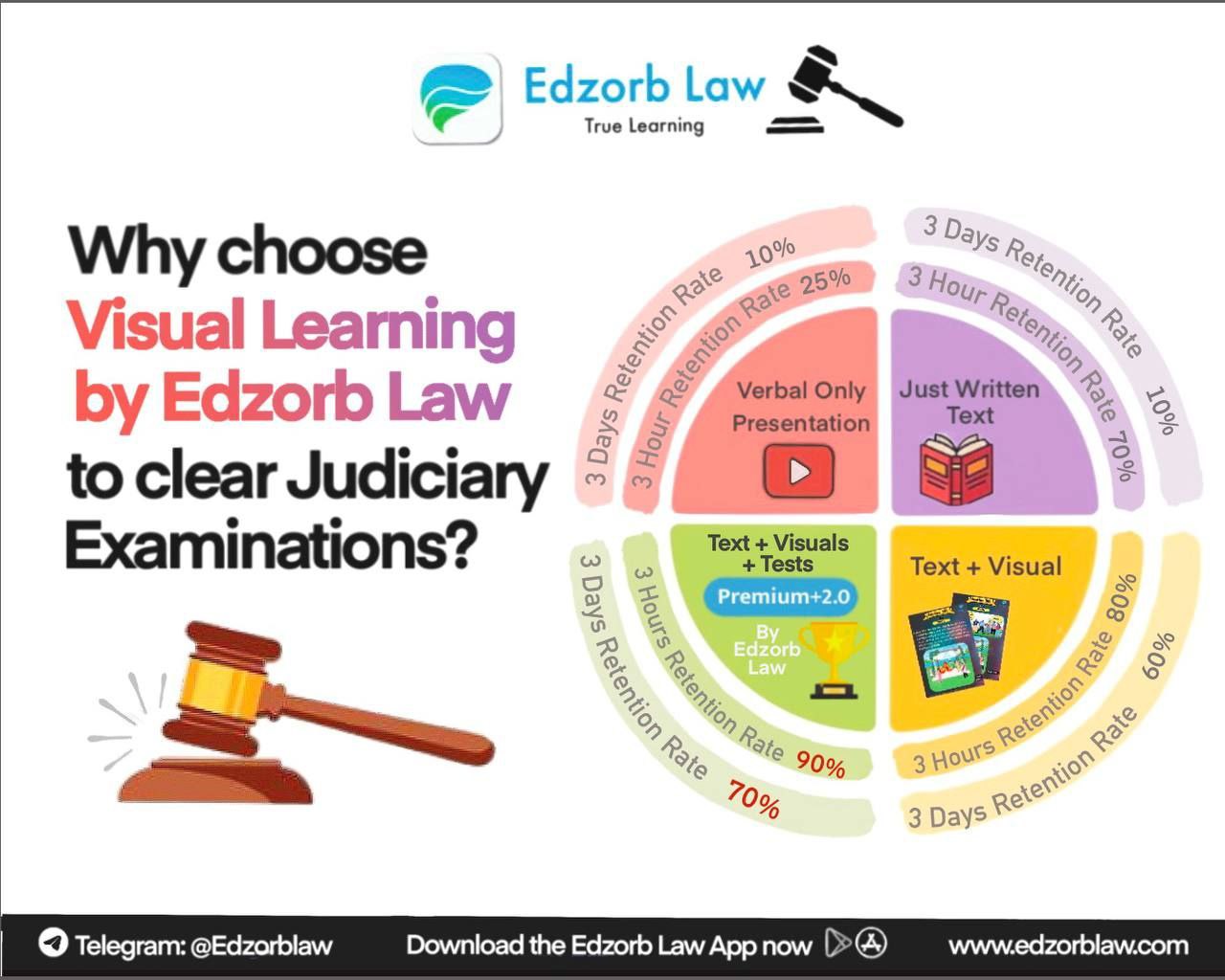
Judicial discretion is a vital tool in ensuring that justice is served in cases where existing laws may fall short. However, its exercise must be judicious and adhere to constitutional boundaries. In addition, Edzorb Law offers helpful resources for judicial exam preparation 📚








 Features
Features






