When we think of the Indian judiciary, towering courtrooms and black robes often come to mind. But the real engine room of India’s legal system lies elsewhere in the District Courts.
These courts serve as the first point of contact for justice for most Indians, handling a wide range of civil disputes and criminal trials. Despite their immense workload and importance, their contributions often go unnoticed.
Understanding their powers, functions, challenges, and significance is key to appreciating why they matter now more than ever.
A Quick Glance at the Indian Judiciary
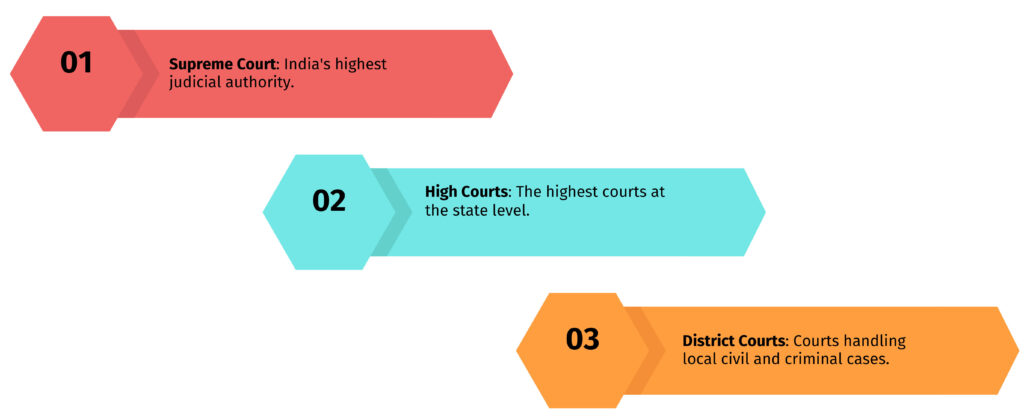
India’s judiciary is a three-tier structure:
- Supreme Court (Topmost)
- High Courts (State level)
- District Courts (Ground level)
Anchored in the Constitution, this system is designed to uphold the rule of law and protect citizens’ rights. While the higher courts set precedent, District Courts are where justice begins for millions.
A Brief History: Colonial Roots, Constitutional Wings
District Courts have evolved from colonial institutions like the:
- Mofussil Diwani Adalat (civil courts)
- Mofussil Nizamat Adalat (criminal courts)
These were the seeds of modern trial courts. The Indian Constitution, under Articles 233–237 (Chapter VI), institutionalized the District Courts, defining their appointment, powers, and control.
The Judicial Layout: Civil vs Criminal Courts
Here’s how it all breaks down at the district level:
Civil Side
- District Judge: Highest civil authority
- Subordinate Judges: Senior Civil Judge, Munsif Court
Criminal Side
- Sessions Judge: Head of criminal court hierarchy
- Magistrate Courts: Judicial Magistrates below Sessions level
Core Functions of District Courts
1. First Stop for Justice
They hear:
- Property disputes
- Criminal cases
- Matrimonial issues
- Guardianship, contracts, and more
2. Interpreting the Law
District Judges:
- Follow statutes and case law
- Use interpretative tools like the literal rule, mischief rule, and purposive approach
3. Safeguarding Fundamental Rights
Yes, even at this level, constitutional rights are enforced, ensuring liberty, equality, and fair treatment.
4. Execution of Judgments
Verdicts don’t end with words. District Courts also enforce orders, issue warrants, and ensure compliance.
5. Administrative Duties
- Oversee subordinate courts
- Handle staffing, case allocation, court logistics
These aren’t just courtrooms, they’re mini justice ecosystems.
Challenges on the Ground

Despite their central role, District Courts face serious systemic challenges:
1. Delays Due to Vacancies
Thousands of posts remain vacant. This slows proceedings, causes adjournments, and frustrates litigants.
2. Poor Infrastructure
- Courtrooms without fans or chairs
- No digital systems or e-filing
- Overcrowded corridors, justice in chaos
3. Shortage of Support Staff
Without clerks, stenographers, and bailiffs, even the best judges can’t function efficiently.
4. Training Gaps
Judges have little time to upskill. Keeping pace with new laws, judgments, and tech is a struggle.
5. Gender Imbalance
The lower judiciary needs more women, especially in family and sexual violence cases, where gender sensitivity is key.
The Way Forward: Building a Stronger Justice Base
If District Courts are to thrive, we need:
Faster Appointments
Speed up judicial selection to fill vacancies without compromising quality.
Digital Courts
Roll out video hearings, e-filing, and AI case tracking to modernize the system.
Continuous Training
Offer regular workshops on new laws, tech tools, and courtroom ethics.
Promote Women in Judiciary
Make courtrooms more diverse and empathetic. Justice must not only be fair, but feel fair.
Why It All Matters
District Courts aren’t just the bottom of the judicial ladder, they’re the foundation of legal faith in India. They’re where the poor seek redress, where property disputes get resolved, where families find closure, and where criminal justice takes its first steps.
A strong, efficient district judiciary means:
- Faster resolution
- Reduced burden on High Courts
- Greater trust in the legal system
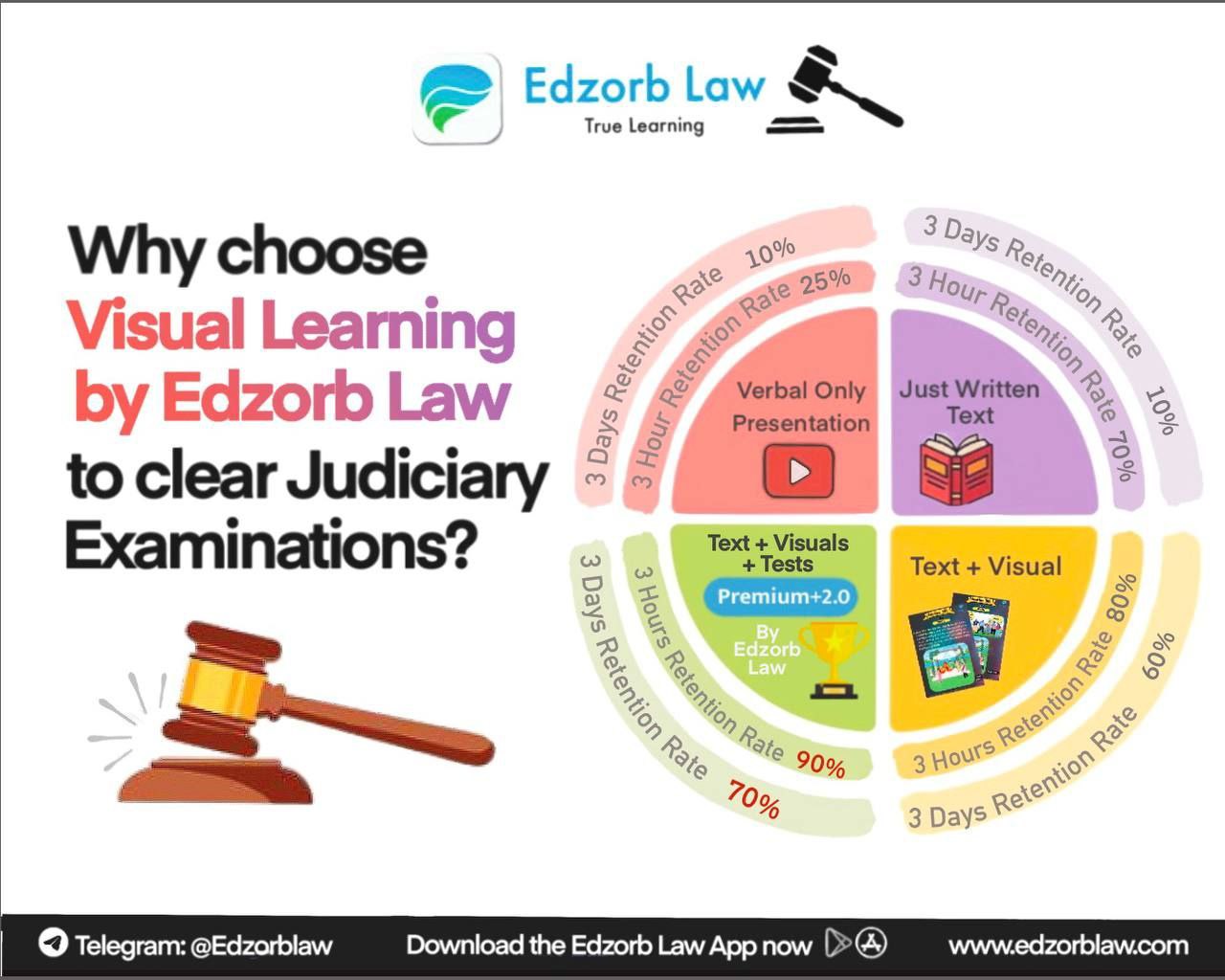
Want to Master the Judiciary System Inside Out?
Whether you’re preparing for judiciary exams, law school, or just curious about how India delivers justice; Edzorb Law is your go-to companion.
Explore:
- Bite-sized notes on judiciary structure
- Flashcards for constitutional provisions
- Real-life case law examples
- Visual memory aids + MCQs to practice on-the-go!
Edzorb Law helps you study smarter, not harder, and makes every topic feel like a courtroom drama you want to binge.

 Podcast
Podcast




 Features
Features






