Judicial activism in India has played a transformative role, shaping the nation’s legal landscape and touching the lives of millions. The judiciary, often seen as the conscience keeper of the Constitution, has stepped in at crucial moments when lawmakers hesitated or faltered, ensuring that justice prevails.
One of the key tools behind this activism has been Public Interest Litigation (PIL), which has empowered individuals and groups to challenge laws and policies that are deemed unjust or harmful.
What is Judicial Activism?
Judicial activism refers to instances where courts interpret laws in a broader social context, often filling legal gaps left by the legislature or executive. In doing so, judges sometimes set new legal precedents or extend existing ones to protect rights, promote equality, and uphold justice.
It’s not just about interpretation; it’s about intervention when necessary.
Key Features:
- Proactive judicial involvement
- Emphasis on public interest
- Progressive interpretation of the Constitution
- Willingness to step in when legislature fails
Famous Examples of Judicial Activism
Vishaka Vs State of Rajasthan (1997)
In the absence of a law on sexual harassment at work, the Supreme Court issued binding Vishaka Guidelines, laying the foundation for the POSH Act, 2013.
Brown Vs Board of Education (1954)
A U.S. case where the court declared racial segregation in schools unconstitutional, transforming civil rights jurisprudence.
Roe Vs Wade (1973)
Another U.S. case that legalized abortion based on the right to privacy, highlighting how courts can influence deeply personal rights.
Why It Matters
Judicial activism has helped:
- Enforce Fundamental Rights
- Strengthen Environmental Protections
- Empower Marginalized Groups
- Safeguard Democracy
From cleaning the Ganga to upholding the right to privacy, activist judgments have redefined Indian law.
Criticism of Judicial Activism
Critics warn that activism can turn into judicial overreach, where judges:
- Encroach upon legislative or executive domains
- Act beyond their constitutional role
- Risk eroding democratic accountability
They argue: Courts are meant to interpret law, not make it.
Striking the Balance: Activism Vs Restraint
Judicial activism walks a fine line. When balanced with judicial restraint, it becomes a force for good.
It must be:
- Rooted in constitutional values
- Guided by legal reasoning
- Mindful of democratic principles
The ideal court? One that knows when to speak, and when to stay silent.
In the Indian Context: A Game-Changer
Judicial activism in India has:
- Protected democratic values
- Supported gender equality
- Enhanced environmental governance
- Amplified the voice of the marginalized
Yes, it’s controversial. But it’s also been transformational.
Final Thoughts: Law That Listens
In a country as vast and diverse as India, judicial activism has proven to be more than just a philosophy, it has been a lifeline. When parliaments delay action and executive power falters, the judiciary steps in as a voice of reason and hope for the people. While not without its flaws, judicial activism, when used wisely, has the potential to drive significant social change and ensure justice for all, especially when other branches of government fail to act.
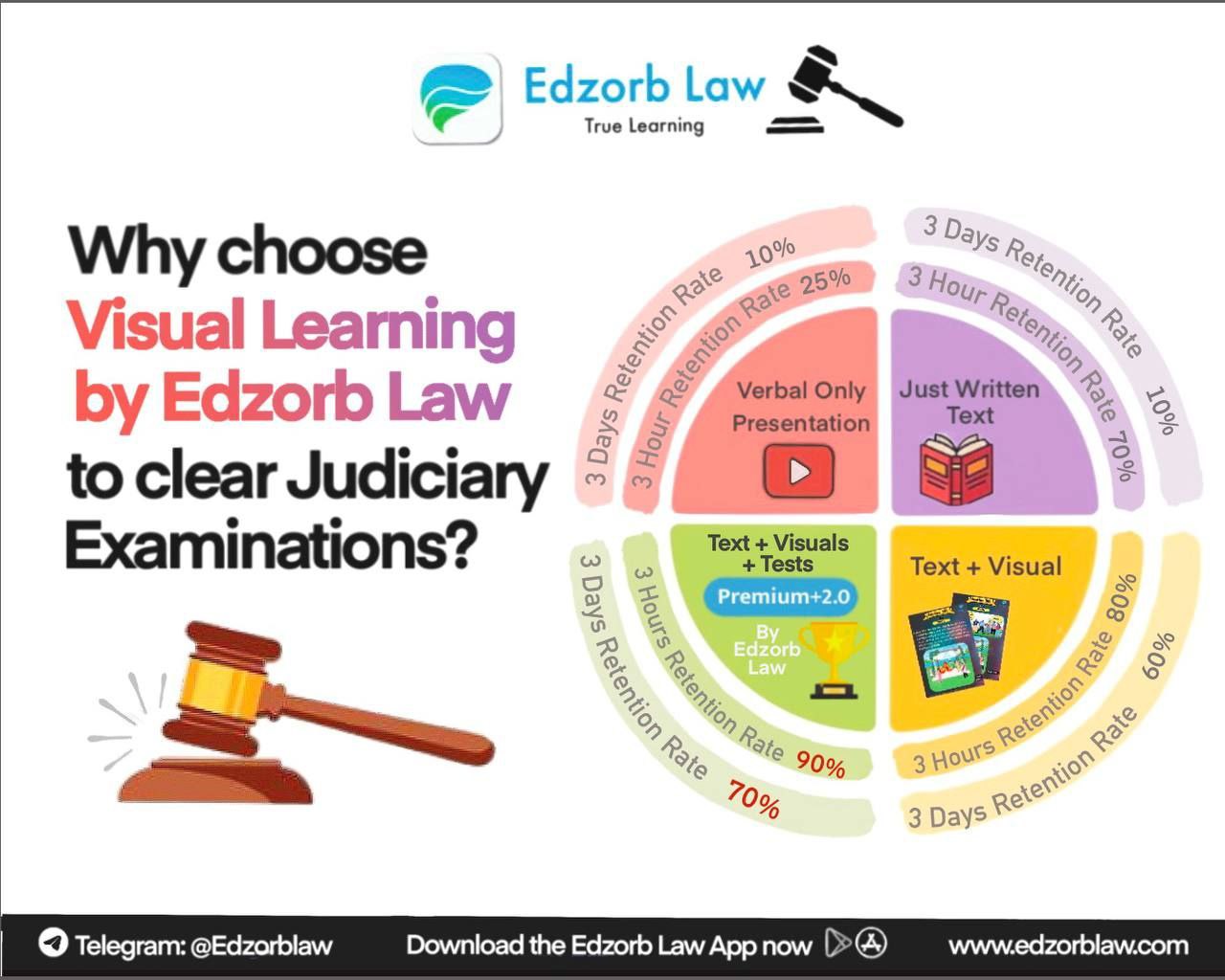
Want to Ace Judicial Reasoning like a Pro?

Whether you’re prepping for the judiciary or want to understand landmark judgments better, Edzorb Law is your one-stop solution.
- In-depth case analysis
- App-based learning with visuals and mnemonics
- Notes that simplify complex concepts
- Learn smart, revise faster, and crack your exam with confidence!
👉 Download the Edzorb Law App Now | Empower Your Legal Journey.

 Podcast
Podcast



 Features
Features






